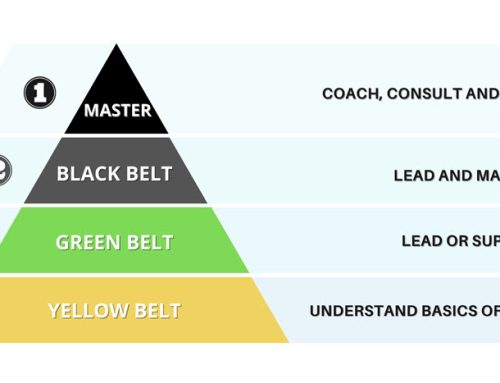
The 8D methodology is a method for solving problems to achieve process and product improvement. It is designed into eight steps (the 8 D’s) and focuses on team. The 8D methodology is used widely across automotive companies, but has with great success been adopted across various other industries.
The 8D is short for Eight Disciplines which was created from the Ford’s TOPS (Team Oriented Problem Solving) program which was first published around 1987.
The eight disciplines are
- D1 – Establish the Team.
- D2 – Describe the problem.
- D3 – Develop an Interim Containment Action.
- D4 – Define / Verify Root Cause.
- D5 – Choose / Verify Permanent Corrective Action.
- D6 – Implement / Validate Permanent Corrective Action.
- D7 – Prevent Recurrence.
- D8 – Recognize the Team.
Obviously, several companies have their different understanding on what they call the steps and so on but that is the basics.
Why Use the 8D Methodology
The 8D methodology is so common in part because it gives your team a steady, easy to learn and systematic approach to unraveling whatever issues might arise at different stages in your production process, projects or business. When correctly applied, you can anticipate these benefits.
- Advanced and improved team oriented problem solving abilities instead of relying on the individual.
- Enhanced understanding and acquaintance with a structure for problem solving.
- The creation and enlargement of a database of previous failures and lessons learned to avoid problems in the future.
- A better understanding of how to use rudimentary statistical tools needed for problem solving.
- The Improvement of effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving.
- A better practical knowledge of root cause analysis (RCA).
- The problem solving determination may be implemented into the processes and methods of the organization.
- Enhanced skills for implementing corrective action.
- Better capacity to recognize essential systemic variations and ensuing inputs for change.
- More sincere and open communication in the discussion of problem solving which increases effectiveness.
- Advancement in management understanding of problems and problem resolution.
How to Apply the 8D Methodology
The 8D method substitutes for inductive and deductive problem solving tools to persistently move forward towards a solution.
Plan and Prepare for the 8D
Appropriate planning will always turn to a great start. So, before the 8D analysis begins, it is always a great idea to ask a professional first for their impressions.
D1 – Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) which involves members from several disciplines. This can also be taken a step further by having two levels of a Cross Functional Team. A principal team which uses data-driven methodologies and Subject Matter Expert (SME) team which involves members, who study, brainstorm and observe.
D2 – Describe the Problem
The 8D method’s first focus is to correctly define the problem using known data and putting it into precise categories for future assessments.
D3 – Interim Containment Action
Before the permanent corrective action has been determined, in the temporary, an action to protect the client can be taken. The ICA is not permanent and is usually removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
D4 – Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be known to take lasting action to eradicate it. The root cause description necessitates that it can be turned on or off, at will.
D5 – Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The Permanent Corrective Action is directed towards the root cause and eliminates or changes the conditions of the process or product that was responsible for the problem. The activities here includes, establish the acceptance criteria which include mandatory requirements and wants, perform a Risk Assessment on the PCA choices, based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA.
D6 – Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
Proper planning is important to effectively implement a lasting change. A project plan should include steps to complete, communication, lessons learned and measurement of success.
D7 – Prevent Recurrence
This stage affords the chance to share and preserve the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, locations, processes, or families. Updating documents, procedures and work instructions are normal at this step to advance future use.
D8 – Closure and Team Celebration
The teams need feedback to let for pleasing closure. Identifying both individual and team efforts and permitting the team to see the past and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process.
Conclusion
The 8D methodology was made to represent the best practices in problem solving. If done correctly, this method not only advances the quality and reliability of your products but also prepares your team for future problems.