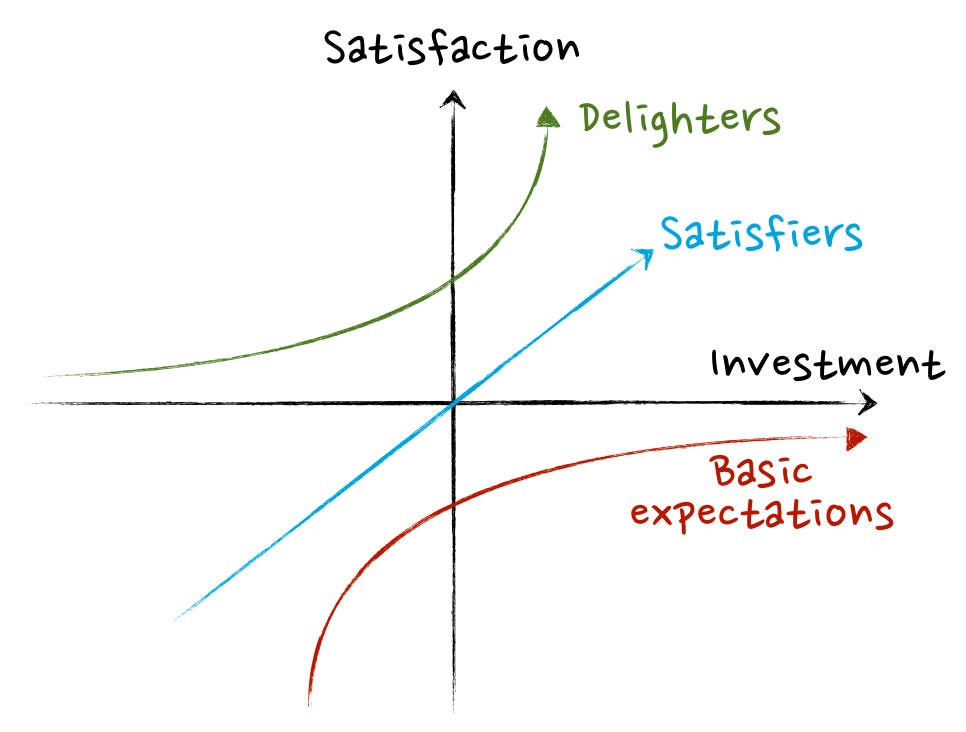
Professor Noriaki Kano developed the Kano model in the 1980s; it is a concept of product development as well as customer satisfaction by classifying customer preferences into five groups. It provides strategies to assist us in comprehending customers’ views on the features of a particular product by simply evaluating two measures of each of the features: the sentiment and the satisfaction. The answers to these measures will definitely fall into one of the Kano model categories; Performance, Attractive, Undesired, Must-Be, Indifferent.
How to Make Use of the Kano Questionnaire Examples and Model
Kano questionnaire examples should be crafted with every feature listed independently. For every feature, typically you show what the particular feature can do with the aid of an interactive wireframe of a prototype, whenever possible. However, do not spend too much time on the prototype; it is just to get the idea across. A lot of people tend to get caught up in the details of the prototype probably because they only like the idea and not how it was being implemented.
The 5 Requirements of Kano Model for Customer Satisfaction
The Kano model has a defined methodology in order to be able to fascinate the customer by exceeding their expectations. Below are the requirements of the Kano model and each of the requirements are given 5 Kano questionnaire examples.
Attractive Requirements
If these requirements exist, it is better. However, if they do not exist, it does not mean that the client won’t be satisfied. These requirements can help you attract more customers to your products or services and also differentiate your services or products from others however, they are not really essential to the success of your business.
Kano questionnaire examples for attractive requirements are;
- A restaurant providing free parking on its premises.
- A car with five years warranty rather than the usual 1 year.
- An airline which offers double miles.
Performance or One-Dimensional Requirements
The performance requirements satisfy the customers if present; moreover, high performance will bring about great satisfaction. That is, the more effective the performance, the bigger the satisfaction derived by the customer and vice versa.
Kano questionnaire examples for one-dimensional or performance requirements include;
- The tastier the meal, the more gratified the customer.
- The more economical a car, the more satisfaction it will bring to the client.
- Comfort is in direct proportion to customer satisfaction.
Obligatory or Mandatory Requirements
These are requirements in which without them, the clients will definitely not be satisfied. The customer would tend to wait for these requirements and demand their presence. They are fundamental attributes of the service or product and without them; the products or services will be considered very unsatisfactory.
Kano questionnaire examples of mandatory requirements;
- All restaurants are required to be hygienic and neat because without this, every customer will never be satisfied.
- A car which is unsafe and could be risky to its passengers definitely does not possess a mandatory requirement which any customer demands.
- If you saw that the paint of an airplane was flaking, would you fly in it? Of course, this does not affect the performance or safety of the airplane however, for an airplane, it is mandatory to look safe in any feature. Meanwhile, if this was a cab or a bus you were taking, it most likely would make no difference to you.
Indifferent Requirements
These are features that do not have any impact whatsoever on the performance or the degree of satisfaction derived by the customer.
Kano questionnaire examples of indifferent requirements;
- Why would it be of concern to the customer of a restaurant if the inventory management system of the restaurant is company A or B?
- How is the driver of a car affected by the color of the internal cable which he does not see?
- Will a client be more satisfied with an airline because of its fuel consumption?
Reverse Requirements
These requirements are perceived to be negative by customers. They have a reverse impact on customer satisfaction.
Kano questionnaire examples of reverse requirements;
- A crowded restaurant with huge queues, might be great for the owner however, unpleasant to the customers.
The fewer varieties and options on an airline menu, the lower the customer’s satisfaction.