Practitioners of lean are in agreement on the 7 wastes of lean. Companies save lots of resources when improvement projects focused on these 7 wastes of lean are carried out. This in return, helps save money and time.
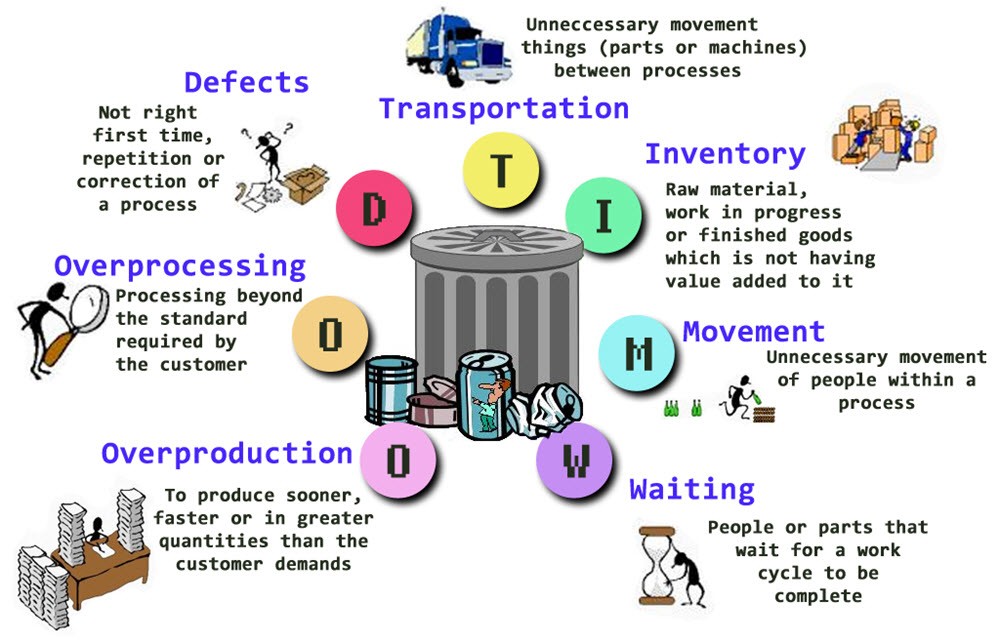
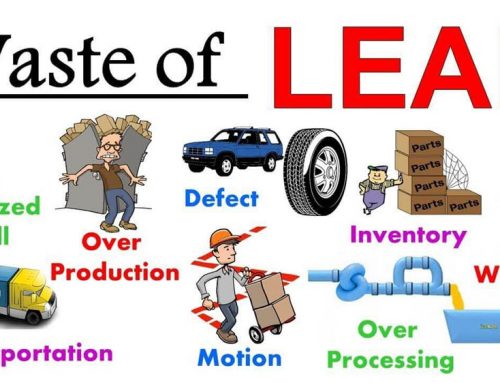
The 7 waste of lean are;
- Transportation
- Inventory
- Motion
- Waiting
- Over-production
- Over-processing
- Defects
These 7 wastes are classes of unproductive work practices.
The 7 Wastes of Lean
Transportation
This is the process of moving goods between several different operations. In the case of an organization that renders services, this can be the moving of data, employees and clients between different locations. So, why is transportation one of the 7 wastes of lean?
- The time of movement costs money.
- There is a possibility of goods misplacement.
- If the product is being moved, no value is added to it.
- The cost of moving the product includes bins, automation, rollers and carts.
- During the movement, product could be damaged.
- Unnecessary loss of energy in moving the product.
Inventory
This involves buying more than is needed and also, building much more than you are selling. So, why is too much inventory a waste?
- Whenever products have issues, the inventory product is suspected and therefore has to be reviewed.
- Inventory unnecessarily takes up limited space.
- Money is spent to store any inventory including shelves, carts, bins and so on.
- Inventory delays problems identification. A lot of times, issues are found with work in progress (WIP) later than the production step which caused the issue.
- Money spent on the inventory could be made use of in more valuable activities.
- The inventory WIP of one product slackens the delivery of another and escalates lead time.
Motion
This is when machines and workers perform excessive movement. This happens during the rel value added stage of the procedure. Below are reasons why motion is one of the 7 wastes of lean.
- It delays communication.
- It could cause damage/ injury as a result of excessive bending, lifting and stretching.
- It results in too much processing period due to reaching, walking and lifting.
Waiting
This is the dead time amid value added phases. Waiting adds significantly to the total processing period of the service/product.
- Waiting time cannot be recovered.
- During waiting, money invested in production sits idle.
- Just like inventory, WIP that is waiting unnecessarily takes up limited space.
- Waiting builds up inventory.
- Waiting slackens the delivery of the product to the client and thus getting paid.
Over-Production
This particular one of the 7 wastes of lean happens when services or products are being provided or manufactured before it is being needed. A lot of organizations over-produce just because they don’t want their machineries and tools to sit idle. Why is over-production one of the 7 wastes of lean?
- It causes errors of scheduling.
- Just like inventory, it makes the organization invest money on products that are not necessary.
- It thwarts a balanced flow of production.
Over-Processing
This is the process of giving too much value to the client or making use of over-kill costly equipment to produce the product.
- The more complex the product, the more likelihoods for defects and mistakes.
- The organization invests unnecessary resources into the acquisition of equipment.
- Repairs and maintenance of the equipment and machinery has more downtime and is more costly than smaller equipment.
- It is more challenging to execute a balanced flow of production because the equipment cannot be moved or because the included features further complicates the flow of production.
- The company invests unnecessary resources into the feature of the added product.
- There is unnecessary training & workers qualification for the equipment and added features.
Defects
This is services or products that do not meet the requirements. Here are reasons why defects are one of the 7 wastes of lean.
- Costs are related with re-inspection, MRB and segregating.
- It decreases workers morale due to constant rework & rebuilding.
- The product rework causes excessive delays, time and costs.
- Client’s disappointment in the corrective actions, rescheduling and the producer’s loss of manufacture capacity.
- Scraping the product results in excessive delay, cost and time.
Lean production is established on a just-in-time production model so as to prevent the waste as a result of excess inventory, waiting and over-production.