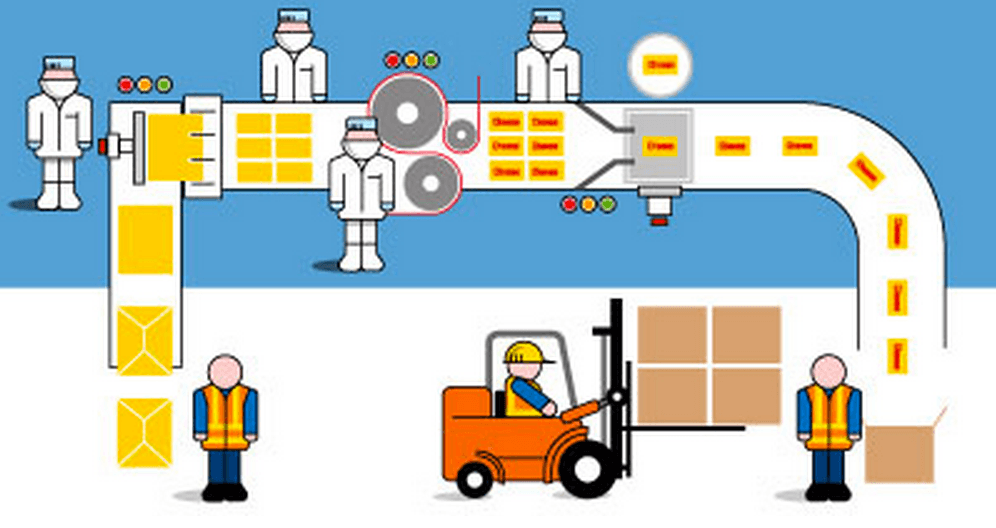
Every company needs a sound flow production plan to maximize productivity. However, for a complex process that covers a wide variety of activities effective production planning is required to ensure that equipment, materials and human resources are available where and when they are needed. Production planning is like a guide that it assists you with where you are heading to and how long it would take you to get there.
Below are some merits of an effective flow production plan and scheduling
- Reduced labor costs by improving process flow and removing wasted time.
- Reduced inventory cost by reducing excessive work-in process inventories and the necessity for safety stock.
- Increased capacity and optimized equipment usage.
- Improved on-time deliveries of services and products.
Key Factors of a Flow Production Plan
Effective planning hinges on a comprehensive understanding of main actions that business manager and entrepreneurs should apply to the process of planning. Here are some instances:
Forecast Market Expectations
You need to evaluate potential sales with some reliability in order to plan effectively. Most businesses do not have firm numbers on future sales. On the other hand, you can forecast sales based on market trends, historical information and/ or established orders.
Inventory Control
Reliable inventory levels feeding the pipeline have to be established and a sound inventory system should be in place.
Availability of Equipment and Human Resources
The period of time permitted between processes so that every order flows within your production line or service is referred to as open time. Flow production planning helps you manage open time, confirming it is well-utilized, whereas being cautious not to create delays. Planning should maximize your operational capacity but not surpass it.
Standardized Steps and Time
Usually, the most effective method to determine your production steps is to plan processes in the order they happened and then include the average time it took to complete the work. Bear in mind that all steps do not occur in sequence and that several may happen at the same time.
You will realize how long it will take to complete the entire process, after completing a process map. Where work is similar or repeated, it is preeminent to standardize the work and time involved. Document related activities for future use and use them as a base-line create future routings and times. This will hasten your planning process considerably.
Risk Factors
Estimate these by gathering historical information on related work experience, materials, listing the real time and failures faced. Conduct a failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) and make sure that controls are put in place to minimize or eliminate them wherever risks are important. This procedure enables you to learn and determine ways to reduce potential problems within your business operations. This type of analysis is commonly found in assembly and manufacturing businesses.
How to plan work
Every other activity is commenced from the flow production plan and each area is reliant on the interaction of the activities. Usually, a plan addresses materials, training, equipment, human resources, capacity and the method or routing to finish the work in a standard time. In order to make good sales forecast, ensure you base it on a history of firm orders.
Key elements to ensure an uninterrupted flow production
- Material ordering
- Equipment procurement
- Bottlenecks
- Human resources acquisition and training
The flow production plan offers a foundation to plan the real work and schedule the specifics of daily activities. You have to address them separately based on their significance as sales orders come in. the significance of the sales order would decide the work flow and when it should be planned. Following, you should estimate if you are set for production or to render the service.
Communicate the Plan
Once you’ve determined that you have met the conditions to begin flow production, you will have to communicate the plan to the workers who would implement it. You can plan the production in a database, software or spreadsheets. Nonetheless, a visual representation is preferred as a means to converse operation plans to floor workers. The plan also has to be presented to workers ahead of time and kept up to date.
Consider Change
Following up with changes to orders is one of the numerous challenges of scheduling and production planning. Changes happen daily. You will have to adjust your plan in line with these changes and advise the plan. Managing change is complex and might take as much effort as creating the original flow production plan. In order to rectify any problems, you will have to follow up with the several department involved in. however, computer software can be helpful in tracking, inventory, changes, equipment and employees.