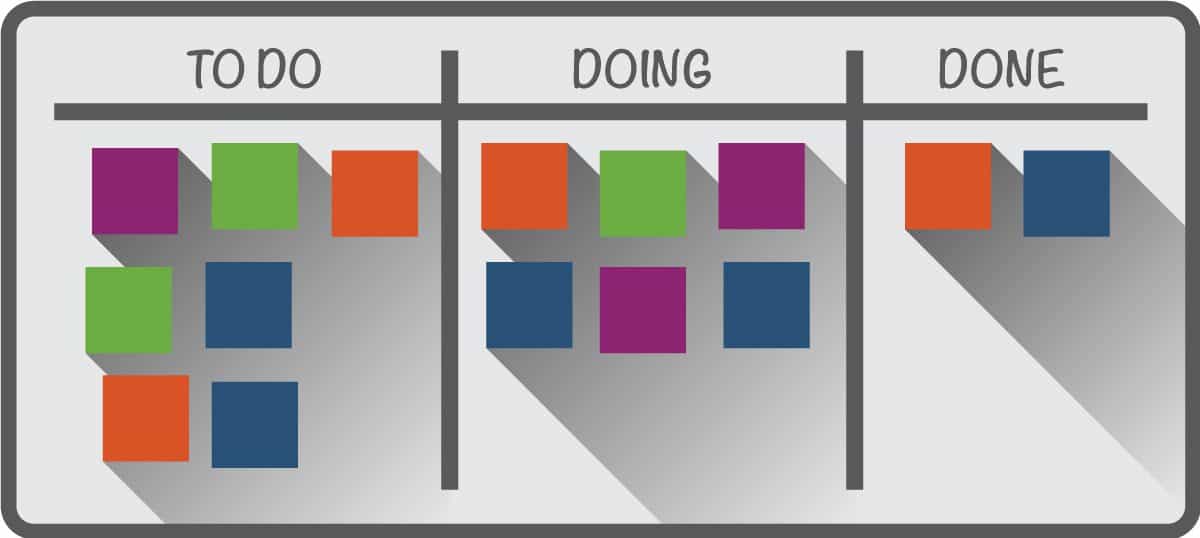
For a successful implementation of Kanban within manufacturing, you must ensure you have set right environment for it. The further you are from ideal situation; the more work is required to implement this system.
Following are ideal situations which should be considered during Kanban implementation steps:
- Keep constant prediction about demand for products.
- Have fewer production variation or utilize several common parts between variations.
- Established the flow for all your processes.
- Use smaller scale dedicated pieces of machinery.
- Capable of making changeovers in short time or use Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)
- Have repeatable and stable production processes or apply Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), Just in Time (JIT) standard operations, and operator-driven quality improvements.
- Collaboration with reliable suppliers in a robust supply chain.
Not complying above conditions does not reflect that Kanban cannot be implemented. It just means that you may need to spend more time evaluating your processes and establishing the correct Kanban system before starting the Kanban implementation steps. Commonly, getting irregular demand and higher number of product variations need to follow a CONWIP (Constant Work in Progress) system.
Do not be discouraged if your environment is not ideal for going ahead with the Kanban implementation steps from day one. Kanban in manufacturing is all about continuous improvements and having to make some adjustment prior to implementation pays out several times in the end.
Making up a Pull Production System
Kanban is part of lean manufacturing and JIT systems. For the pull production system that ensure JIT manufacturing, then it is all about controlling what, when, and how much that comes through the production. Its aim is to ensure that only the required product or volume needed by the customers is produced at the time it is needed. To make it possible, Kanban follows JIT to make a pull system.
There are number of Kanban rules that can support you during your Kanban implementation steps to create a pull production system:
- Each process collects products from the earlier processes based on their needs.
- Each process gets information from the earlier process of what is next to manufacture.
- Each process only delivers what the next process needs.
- Without a Kanban permission, no products can be moved or produced.
- Defects must be detected and removed as close to the source as possible and not be sent to the following processes.
Different Kanban Systems for Manufacturing
After setting up the right environment, next step is to look for the correct approach to implement a Kanban system in manufacturing. There are 4 common approaches of Kanban system for manufacturing that often works in most businesses. You can select one or combine these approaches the systems fit within your organisation. These approaches are outlined below.
Kanban cards approach
Kanban cards approach is simply use of cards as signals. These are cards fixed to the collection of materials as it moves around the production line. Generally, for each product, there are 2 to 3 cards in the system. But if you deal with larger collections then there could be more cards. Typically, these cards have the information about the product like what product it is, where and how to use it, and what quantity is required.
Kanban bins approach
This is where Kanban bins work like Kanban cards. But rather than using cards fixed to the materials under the process, the bins or containers which store materials are the actual Kanban. When they get emptied, they returned to last step as a signal to produce and fill them up again. These bins can also be tagged with same information such as cards. If you chose to use Kanban bins though, the individual bins must be for one particular material only.
CONWIP approach
The Kanban Continual Work in Progress (CONWINP) approach is closely resembled shelves restocking in supermarket. The Kanban is the reallocation of products or parts, the empty shelves, or floor spaces. The production of this system depends on demand. CONWIP helps manufacturers lower scale of inventory as compared to use of Kanban cards or bins.
E-Ban and Fax-Ban approach
With all technology accessible today, it is easy to create a paperless Kanban system. This is possible by use of QR code scanners or it could be machines that use electronic communication with each other. E-ban and Fax-ban offer companies more relaxation and saves time as cards and bins do not need to move physically in the process. Everything is managed through electronical communication.
But be aware, Kanban approaches do not work wonders overnight. It requires right training and information for your employees. Be patient as you develop your Kanban system and continually improve it. You will the see the benefits it will bring to your manufacturing.