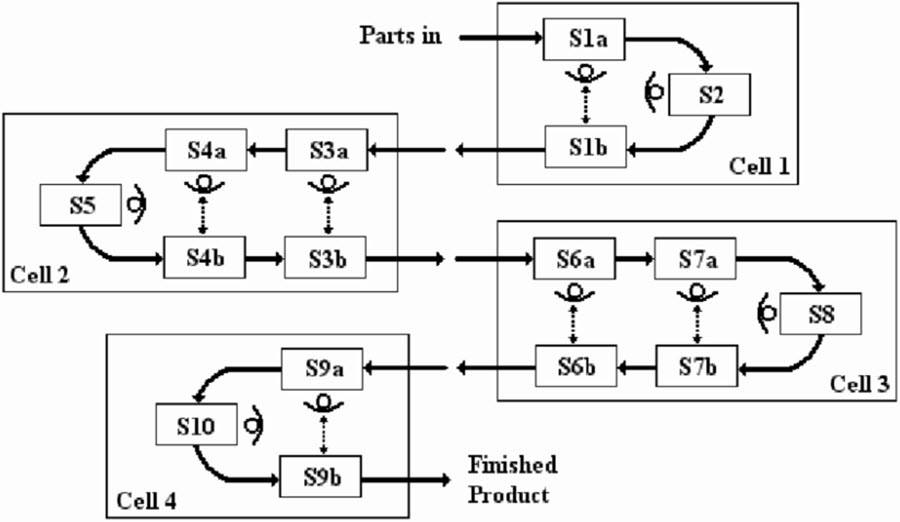
Cellular manufacturing is considered as an essential part of lean manufacturing. It deals with manufacturing products in small batches to aid continuous production process. Cellular manufacturing follows the principle of group technology, a term introduced by Frederick Taylor, that means that analogous products having similar properties are grouped together and so does the equivalent machines. This results in higher productivity than that achieved through conventional manufacturing methods.
Cellular manufacturing involves breaking down the manufacturing process into various steps and organize them into different groups depending upon their complexity and similarity. First of all the value stream map is formed that involves all the steps required to be carried out in the production process. All the processes and personnel are brought together in one confined unit which is then defined as a “cell”. In this way the workstations and equipment are in proximity with each other due to their arrangement in a flow sequence which result in least transport and deferment.
Method of Implementation
The traditional implementation process of cellular manufacturing includes the following stages.
Assessment of existing conditions
First step in implementation of cellular manufacturing is to analyze and assess current working conditions including product and mechanism. Some organizations utilize value stream mapping at this stage to draw the layout for better understanding of product flow. After this cycle time and lead times are measured and inscribed in the worksheets for graphical representation of relation between hand operated process time, equipment process time. It helps in calculating attainment underneath cellular product flow.
Conversion into a cellular outline
Next step in cellular manufacturing involves the conversion of manufacturing area into cellular or work cell lay out. This is done by rearrangement of operation components so that transforming steps of various types are directed contiguous to each other. For this purpose the equipments or machinery is rooted in C or U shape to minimize operator’s activity and motion. Some of the important techniques that aid an efficient cellular outline or lay out include:
- Automation: It is the convection of human perception to computerized machines so they are capable of starting, stopping, loading and unloading automatically on their own. For example, in Jidoka lean manufacturing, the machines are designed so as to stop automatically when a defective production is identified and signal is generated automatically.
- Single minute exchange of die (SMED): It allows the organization to transform machinery or an operation to form disparate product type. However, a sole cell can form different product type without machinery changeovers. This helps the organization reciprocate customer’s changing requirements.
- Suitable sized machinery: Conversion into a cellular layout prefer small equipment rather than large ones as they require small space and are easy to move so they can be used at different locations as and when required.
Continuous process improvement
The last and final step in implementation of cellular manufacturing is continuous process improvement. It includes regulation of cell processes to improvise manufacturing time, cost and quality. There are different lean manufacturing tools that are used to prevent losses associated with equipment such as unplanned down time and speed arrest. These are tools as Kaizen, Six sigma and TPM.
Benefits of Cellular Manufacturing
Cellular manufacturing has many advantages compared to traditional manufacturing. Some of those are listed below.
- It reduces the startup time, which is the time required for preparation of the machinery or equipment to perform its function.
- It decreases both the time and cost that is required in material handling. Material handling refers to techniques of moving, storage and controlling of different materials at minimal cost. Therefore, in cellular manufacturing, this cost is reduced due to need of less man power and less transportation of materials from one area to another.
- In cellular manufacturing unnecessary machines and equipments are taken out and a single machine can manufacture different products. Thus it improvises machine utilization because idle time is reduced due to less start up time.
- It also minimizes lead time associated with production because of less startup time, material handling time and improved material utilization.
- As cellular manufacturing takes place in a sole area and under the supervision of small team there are lesser chances of any mistakes or defects. Thus it improves product quality and ultimately results in customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
To conclude, cellular manufacturing split up complex processes into different smaller components which are easy to analyze and handle. It improves the production flow and reduces lead time which results in customer satisfaction.